Starting your own micro-small business and freelancing job can be exciting because of the endless opportunities. However, it can also be scary because of all the risks. One of the things you worry about is the taxes you must pay, and how to do it.
This article aims to be your guide with regards to taxes required to be filed and paid by sole proprietors of micro and small businesses, as well as freelancers, self-employed and professionals.
Please note that this article is applicable for the following: Individual Purely Sole Proprietor of Business, Freelancer, Independent Contractor, Self-Employed and Professional
Terms and Definition
If you are new to this kind of discussion, here are some basic terms and what it means.
Sole Proprietor
A sole proprietor is the solo owner of a business such as the owner of a business engaged in providing service, such as salon, spa, restaurant, food delivery or food kiosks, travel agency, manpower agency, rentals, etc., or engaged in sale of goods, such as retailers, wholesalers, etc., both online (or thru the internet) or offline (with physical stores).
Freelancer / Independent Contractor / Self-employed
This is a type of individual who provide their service, time and skill but are not professionals or licensed by the Philippine Regulatory Commission (PRC) such as artists, reporters, models, IT / Programmers, sales agent, etc., both online (or thru the internet) or offline (with physical office).
Professional
This somehow similar with the previous, the difference is they have the Philippine Regulatory Commission (PRC) ID and are considered licensed professional such as doctors, lawyers, engineers, architects, real estate broker, insurance broker, accountants, etc., both online (or thru the internet) or offline (with physical office).
Taxes Applicable
Before you read on and start filing your taxes, it is important that you check your BIR Form 2303 – Certificate of Registration, to check if the tax types I will enumerate below are shown in under the “tax type” of your BIR Form 2303. The taxes shown in your BIR Form 2303 “tax type” are the required taxes to be filled for your specific company. Below is a sample BIR Form 2303- Tax Type:

Now that we know the terms and definition, and have discussed the importance of checking your own BIR Form 2303 – Tax Types, let us now discuss the type of taxes applicable to sole proprietors, freelancers, self-employed, independent contractor and professional.
Here are the taxes that may apply, in general:
- Income Tax
- Business or Sales Tax
- Withholding Tax
1. Income Tax
This type of tax is applicable to net taxable income or gross sales/receipts. There are two ways to compute income tax for sole proprietors, freelancers, self-employed, independent contractor and professional:
1st – Using Graduated Income Tax Rates

The computation of net taxable income for this type is as follows:

2nd – Using 8% Income Tax Rate
The computation of net taxable income for this type is as follows:

Important Note:
- This type of special rate (8% income tax) is only applicable and allowed to individual with Yearly Gross Sales/ Receipts below P3,000,000.00
- To avail of this special income tax rate of 8%, you need to your intention or update your registration with the BIR.
- Once approved, the business or sales tax of Percentage Tax will be removed.
BIR FORM:
- Quarterly: BIR Form 1701Q
- Yearly: BIR Form 1701A
REQUIRED ATTACHMENT, in general and if applicable:
- Copies of Tax Credit Certificates such as BIR Form 2307
- Esubmission of SAWT – Summary Alphalist of Withholding Taxes
DEADLINE FOR FILING AND PAYMENT: In general following calendar year:
- Quarterly:
- May 15 for the first quarter of the current year
- August 15 for the second quarter of the current year
- November 15 for the third quarter of the current year
- Yearly: April 15 of the following year
2. Business or Sales Tax
This type of tax is applicable to sales or receipts. There are two types of sales or business tax, in general, applicable to sole proprietors, freelancers, self-employed, independent contractor and professional:
- Percentage Tax, also known as NONVAT.
- Value-Added Tax, also known as VAT.
Important Note:
This business or sales tax will apply to individuals who are not qualified to avail 8% Income Tax and/or pays regular Graduated Income Tax.
a. NONVAT or Percentage Tax
It is a type of tax applicable to individual with yearly gross sales or receipts of less than P3,000,000.00 and pays regular Graduated Income Tax from 0 to 35%.
Computation:
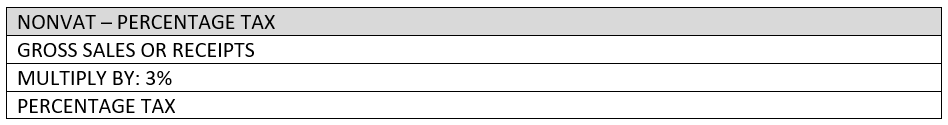
BIR FORM:
- Quarterly: BIR Form 2551Q
DEADLINE FOR FILING AND PAYMENT: In general following calendar year:
- Quarterly:
- April 25 of the current year – for the first quarter
- July 25 of the current year -for the second quarter
- October 25 of the current year for the third quarter
- January 25 of the following year for the fourth quarter
b. VAT or Value-Added Tax
It is a type of tax applicable to individual with yearly gross sales or receipts of more than P3,000,000 or chooses to be VAT registered regardless of amount of sales.
There are two taxes to be considered:
- Output VAT – is computed as follows: Sales x 12%. It is a VAT imposed on sales.
- Input VAT – is computed as follows: Purchases x 12%. It is a VAT imposed on purchases or expenses.
Computation:
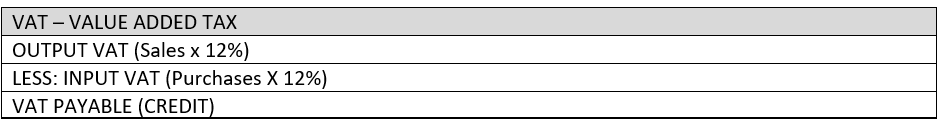
BIR FORM:
- Monthly: BIR Form 2550M
- Quarterly: BIR Form 2550Q
REQUIRED ATTACHMENT, in general and if applicable:
- Quarterly: Esubmssion of Summary List of Sales and Purchases (VAT RELIEF)
DEADLINE FOR FILING AND PAYMENT: In general following calendar year:
- Monthly: 20th day of the following month
- Quarterly:
- April 25 of the current year – for the first quarter ending March 31
- July 25 of the current year -for the second quarter ending June 30
- October 25 of the current year for the third quarter ending September 30
- January 25 of the following year for the fourth quarter ending December 31
3. Withholding Tax
It is a type of tax deducted on certain payments and remitted to BIR. The taxpayer acts as withholding agent of the BIR by declaring income of our vendors/suppliers and collecting advance tax in behalf of BIR.
TYPES OF WITHHOLDING TAX, if applicable:
- Withholding Tax on Compensation – it is a tax withhold or we deduct from payments of salary to our employees, if applicable.
- Withholding Tax on Certain Payments to Vendors (Expanded) – it is a tax withhold or we deduct from payments to our vendors or suppliers, if applicable, such as rental, commission, professional fee, contractors, etc.
COMPUTATION:
- WITHHOLDING TAX ON COMPENSATION

- WITHHOLDING TAX ON CERTAIN PAYMENTS (EXPANDED), example: RENTAL

BIR FORM:
WITHHOLDING TAX – COMPENSATION
- Monthly: BIR Form 1601C
- Yearly: BIR Form 1604-C
WITHHOLDING TAX – EXPANDED
- Monthly: BIR Form 0619E
- Quarterly: BIR Form 1601EQ
- Yearly: BIR Form 1604-E
REQUIRED ATTACHMENT, in general and if applicable:
WITHHOLDING TAX – COMPENSATION
- Yearly:
- Esubmission of Alphalist of Employees
- Distribution of BIR Form 2316 to employees
- Substituted Filing of BIR Form 2316 to BIR, if applicable
WITHHOLDING TAX – EXPANDED
- Quarterly:
- Distribution of BIR Form 2307 to payees/vendors/suppliers
- Esubmission of QAP – Quarterly Alphalist of Payees
- Yearly:
- Esubmission of Alpahlist of Payees
DEADLINE FOR FILING AND PAYMENT: In general following calendar year:
- Monthly: Every 10th of the following month
- Quarterly:
- April 30 of the current year – for the first quarter ending March 31
- July 31 of the current year -for the second quarter ending June 30
- October 31 of the current year for the third quarter ending September 30
- January 31 of the following year for the fourth quarter ending December 31
- Annual:
- FOR COMPENSATION: BIR FORM 1604C – January 31 of the following year
- FOR EXPANDED: BIR FORM 1604E – March 1
I hope this article has been helpful for you to have a quick basic guide and summary of what taxes to file and pay as sole proprietors of micro and small businesses, as well as freelancers, self-employed and professionals. Need help in preparing these forms, computations and organizing your records? Check out our complete Tax Accounting Software and our Payroll Software if you have employees.


Leave a Reply