BIR Form 1601C pertains to Monthly Remittance Return of Income Taxes Withheld on Compensation. It is the tax return used in reporting and remitting the taxes applicable to employees of a registered taxpayer who is also an employer.
Under our Tax Code, Section 79, it states that every employer paying salaries must deduct and withhold tax from the employee’s salary except for minimum wage earner. However, although minimum wage earner is exempt from paying tax, the employer still needs to report the list of employees and their corresponding salary or wage covered under the minimum wage.
As such, whenever you hire an employee for your business, self-employment, or practice of profession, you must comply to the rules on withholding tax on compensation. As an employer, you will be responsible in computing the applicable tax on the employee’s salary and remit such tax to the Bureau of Internal Revenue (BIR) monthly using BIR Form 1601C Monthly Return on Withholding Tax Compensation. At the same time, for employees covered by minimum wage earner, although there is no tax applicable, you must still report the corresponding amount of salary and other benefits in the monthly BIR Form 1601C.
This article will not discuss how to compute salary or payroll and withholding tax of employees. To automate this part of the process, subscribe to MPM Payroll Software, click here. Instead, this article will focus on understanding and how to fill-out BIR Form 1601C Monthly Withholding Tax on Compensation return.
What is Compensation?
First let us define what is compensation.
Compensation is any renumeration for services performed by an employee for his employer under an employee-employer relationship. Also referred to as salary or wage and supported by an employment contract.
And as an employee, the employer has the obligation to:
- Withhold tax and remit the amount to the BIR; and
- Withhold and remit the employee-employer share to SSS, Philhealth and Pag-ibig Benefits.
One of the differences between an employee-employer relationship versus hiring a freelancer is that an Employee is subject to Withholding Tax Compensation while a Freelancer is subject to Withholding Tax Expanded. As such, freelancer is different from an employee and is not part of this article.
There are two kinds of compensation:
- Regular compensation – which pertains to the basic pay.
- Supplemental compensation – which is any addition to the regular compensation such as overtime pay, commission, profit sharing, fringe benefit to rank and file, hazard pay, bonuses, etc.
In addition, compensations are either taxable or non-taxable:
- Taxable – which pertains to employee’s compensation income that are subject to withholding tax.
- Non-Taxable – which pertains to employee’s compensation income that are exempt from withholding tax such as:
- Other benefits or bonuses of not more than P90,000 each year.
- Employee’s share in GSIS, SSS, Medicare (Philhealth) and Pag-ibig contributions.De minimis benefitsEmployee’s Compensation covered by Minimum Wage Earner.
- Employee’s Compensation not exceeding P250,000 per year.
Consider above information when computing payroll or salary and corresponding withholding tax on compensation. To automate this process, subscribe to MPM Payroll Software, click here.
Tax Rate on Withholding Tax Compensation
Withholding on Compensation Tax rate is the same as the rate in the tax bracket used for Individual Taxpayer.
Under the TRAIN Law, below are the applicable tax bracket rates beginning January 1, 2023, and onwards, which the year of writing of this article:
For Daily, Weekly, Semi-Monthly and Monthly Withholding Tax Table
| Compensation Range | Prescribed Withholding Tax | |
|---|---|---|
| Daily | 0.00 – 685.00 | 0.00 |
| 685.00 – 1,095.99 | 15% over 685.00 | |
| 1,096.00 – 2,191.99 | 61.65 + 20% over 1,096.00 | |
| 2,192.00 – 5,478.99 | 280.85 + 25% over 2,192.00 | |
| 5,479.00 – 21,917.99 | 1,102.60 + 30% over 5,479.00 | |
| 21,918.00 and above | 6,034.30 + 35% over 21,918.00 | |
| Weekly | 0.00 – 4,808.00 | 0.00 |
| 4,808.00 – 7,691.99 | 15% over 4,808.00 | |
| 7,692.00 – 15,384.99 | 432.60 + 20% over 7,692.00 | |
| 15,385.00 – 38,461.99 | 1,971.20 + 25% over 15,385.00 | |
| 38,462.00 – 153,845.99 | 7,740.45 + 30% over 38,462.00 | |
| 153,846.00 and above | 42,355.65 + 35% over 153,846.00 | |
| Semi-monthly | 0.00 – 10,417.00 | 0.00 |
| 10,417.00 – 16,666.99 | 15% over 10,417.00 | |
| 16,667.00 – 33,332.99 | 937.50 + 20% over 16,667.00 | |
| 33,333.00 – 83,332.99 | 4,270.70 + 25% over 33,333.00 | |
| 83,333.00 – 333,332.99 | 16,770.70 + 30% over 83,333.00 | |
| 333,333.00 and above | 91,770.70 + 35% over 333,333.00 | |
| Monthly | 0.00 – 20,833.00 | 0.00 |
| 20,833.00 – 33,332.99 | 15% over 20,833.00 | |
| 33,333.00 – 66,666.99 | 1,875.00 + 20% over 33,333.00 | |
| 66,667.00 – 166,666.99 | 8,541.80 + 25% over 66,667.00 | |
| 166,667.00 – 666,666.99 | 33,541.80 + 30% over 166,667.00 | |
| 666,667.00 – and above | 183,541.80 + 35% over 666,667.00 |
For Annual or Yearly Tax Table
| Net Taxable Income | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| 0.00 – 250,000.00 | 0.00 |
| 250,000.00 – 400,000.00 | 15% over 250,000.00 |
| 400,000.00 – 800,000.00 | 22,500.00 + 20% over 400,000.00 |
| 800,000.00 – 2,000,000.00 | 102,500.00 + 25% over 800,000.00 |
| 2,000,000.00 – 8,000,000.00 | 402,500.00 + 30% over 2,000,000.00 |
| 8,000,000.00 – and above | 2,202,500.00 + 35% over 8,000,000.00 |
How to Prepare BIR Form 1601C Monthly Withholding Tax on Compensation?
Now that we know what compensation is, let us now learn how to prepare BIR Form 1601C.
To prepare BIR Form 1601C, you must first have a copy of the monthly payroll register which shows the payroll computation for the month, such as below sample:
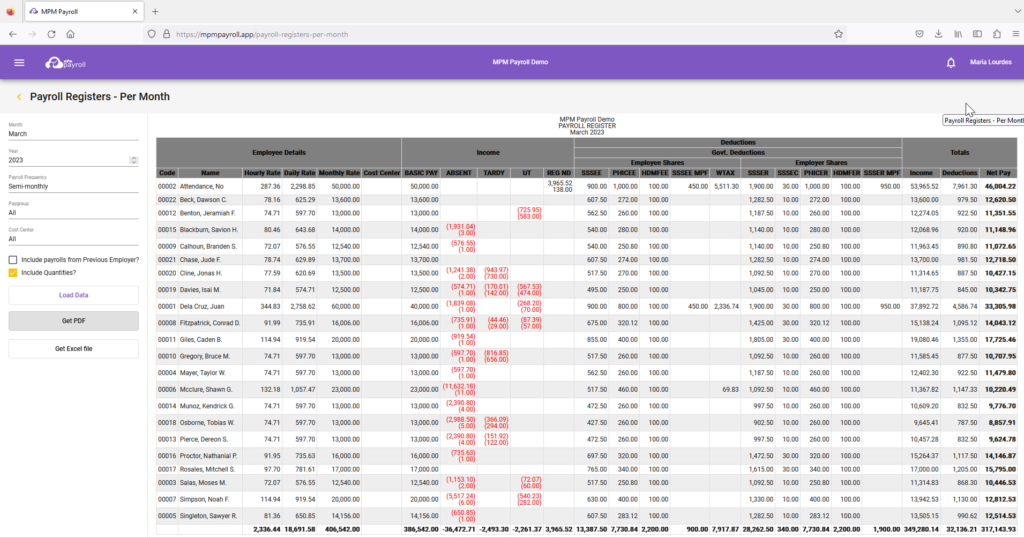
To automate this part of the process, subscribe to MPM Payroll Software, click here.
Like sample above, a payroll register will show you the list of employees and corresponding breakdown of compensation and deductions, such as withholding tax on compensation and mandatory government contributions.
The said payroll register is going to be use in preparing BIR Form 1601C such as below:
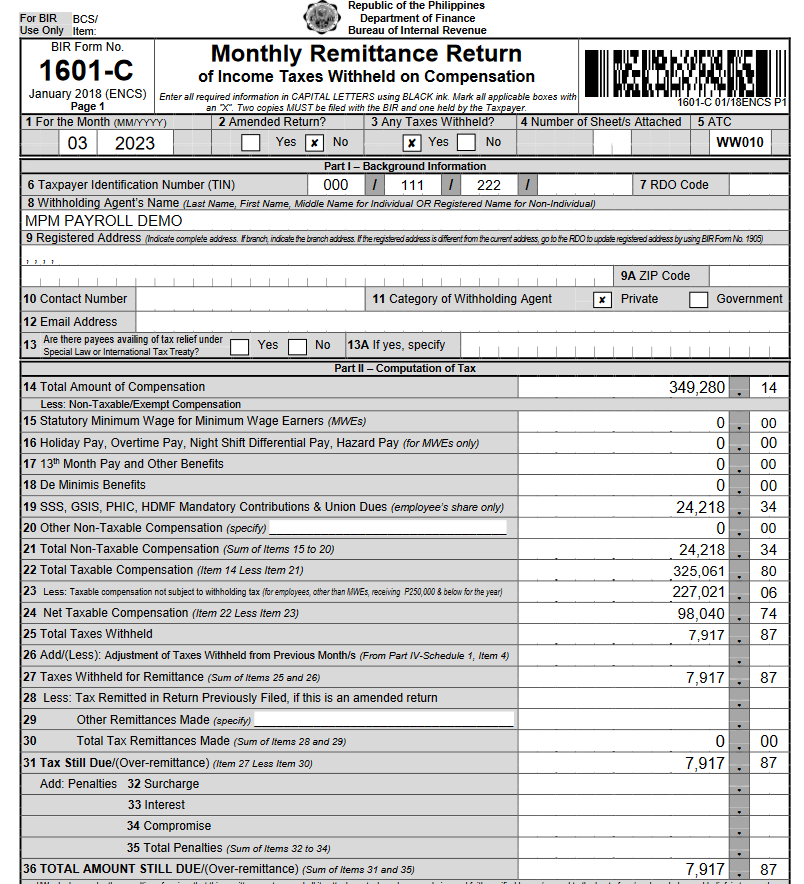
Note: Above sample BIR Form 1601C is prepared automatically by MPM Payroll Software:
Let us enumerate and describe the relevant section of BIR Form 1601C for better understanding:
Item 1 – pertains to the “month and year”. Example: 03 2023 means March 2023
Item 2 – click “No” by default unless you are amending.
Item 3 – click “Yes” if there’s tax due or withholding tax compensation withhold and payable. Otherwise click “No.”
Item 6 to 12 – fill-in your information
Item 13 – click “no” by default unless applicable.
Item 14 – pertains to the salary or wages of all employees regardless taxable or non-taxable.
Item 15 – pertains to the regular compensation or basic pay of all employees covered under minimum wage earner
Item 16 – pertains to supplemental compensation of employees covered under minimum wage earner such as holiday pay, overtime pay, night shift differential pay, and hazard pay
Item 17 – pertains to all employee’s bonuses and other benefits including 13th month pay considered non-taxable and within the P90,000 per year ceiling.
Item 18 – pertains to the additional small value benefits considered and included in the list of de minimis benefits.
Item 19 – pertains to the employee’s share on GSIS, SSS, Philhealth, and Pag-ibig contributions considered non-taxable.
Item 21 – it is the total amount of non-taxable compensation computed by the sum of items 15 to 20.
Item 22 – computed by deducting total compensation (item 14) less total non-taxable compensation (item 21). It pertains to compensation considered taxable.
Item 23 – pertains to compensation of employees that falls within P250,000 per year and below compensation income.
Item 24 – it is the difference of item 22 and 23.
Items 25, 27, 31 and 36 – it is the total amount of tax you withhold from employees and will remit to BIR based on your computation and tax rate bracket.
Where to File BIR Form 1601C?
You may file BIR Form 1601C as follows:
- Mandatory eFPS – pertains to Electronic Filing and Payment System of the BIR. If mandated eFPS filer, you must file via eFPS. EFPS website is https://efps.bir.gov.ph/
- eBIRForm – if not mandated to be eFPS, you may file BIR Form 1601C using electronic BIR Forms (eBIRForm) System of the BIR. Click here to download version as of drafting this article or visit BIR Website for latest version.
Alternately, if not mandated to use eFPS, you may use MPM Accounting Software (MAS) for automatic creation and filing of BIR Form 1601C provided your also a subscriber of MPM Payroll Software (MPS). If not MPS subscriber, BIR Form 1601C can still be filed in MAS but you need to manually prepare the BIR Form 1601C. Try both software for 30 days free trial here: https://mpm.ph/tax & https://mpm.ph/payroll
Deadline for Filing and Payment of BIR Form 1601C
In general, the deadline for filing and payment of BIR Form 1601C is on or before 10th of the following month. But here is a more detailed list of deadlines:
| Month Covered | eBIR Forms | eFPS |
|---|---|---|
| January | February 10 | Group A: Fifteen (15) days following end of the month. Group B: Fourteen (14) days following end of the month. Group C: Thirteen (13) days following end of the month. Group D: Twelve (12) days following end of the month. Group E: Eleven: (11) days following end of the month. |
| February | March 10 | |
| March | April 10 | |
| April | May 10 | |
| May | June 10 | |
| June | July 10 | |
| July | August 10 | |
| August | September 10 | |
| September | October 10 | |
| October | November 10 | |
| November | December 10 | |
| December | January 15 of next year |
Where to Pay BIR Form 1601C?
You may pay BIR Form 1601C using one of the following:
- AABs – which stands for Authorized Agent Banks. This is an over-the-counter payment in the bank accredited by the BIR Regional District Office (RDO) where you have registered.
- Online Payment – you may pay BIR Form 1601C using Myeg.ph and PayMaya; or via online banking such as with Landbank, Development Bank of the Philippines (DBP) or Unionbank. See options here: https://www.bir.gov.ph/index.php/eservices/epay.html
That’s it. You have just learned the basics about BIR Form 1601C Monthly Return for Withholding Tax on Compensation.
I hope this article gave you relevant information. Feel free to comment or ask question below. If you liked this article, please share it!
